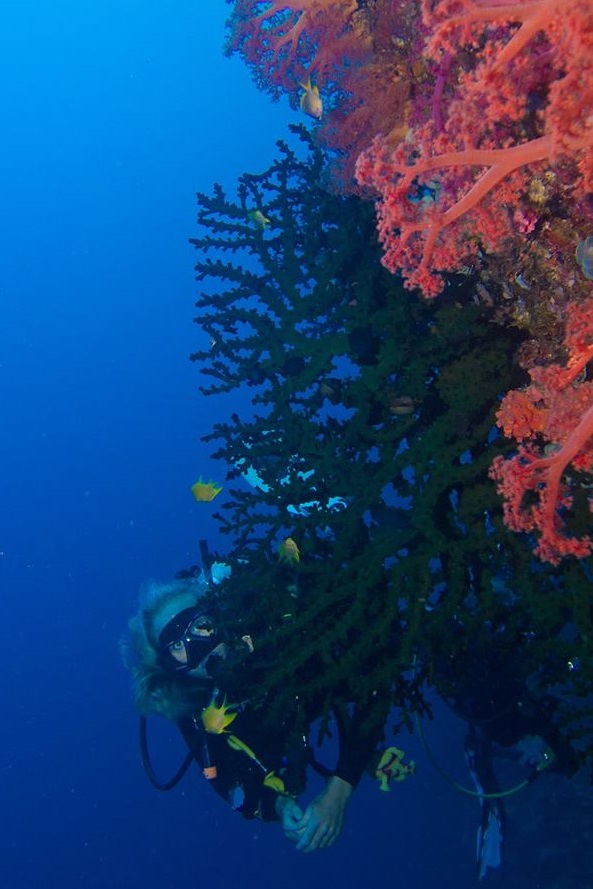
As a diver, you have hopefully been told multiple times in the Divemaster’s briefings not to touch, chase or collect any underwater marine life. But maybe not all Divemasters have explained why this is.
The effects of touching marine life are not always so obvious and a lack of knowledge might pursue those who are curious causing further harm. Touching fish, animals or corals can be as damaging in the long run as intentionally killing or catching them.

Many underwater creatures such as turtles, rays and many species of sharks rely on bio-films (protective slime) to keep away infections. By touching, we can damage this film. Even the different bacteria we have on our hands can ‘eat away’ this protective film and can cause the animal to be more susceptible towards infections, which in the worst case may lead to death.
Corals are equally fragile. The slightest contact can damage the coral polyps’ hard exterior. This leaves the polyps with a reduced immunity which in its turn can lead to the polyp to die off completely. Of course the more polyps are damaged, the bigger the effect on the coral colony.
The damage humans can do as divers and snorkelers alike is very evident. Not only through poor buoyancy control or carelessness by stepping on the reef, but also the sunscreen we wear before going in to the water can damage the reef more than most might know. Sunscreen in particular can damage vast amounts of reef in popular dive or snorkel spots, since the sunscreen will wash off and will do exactly the same to the coral as it would to your skin. The difference is that coral needs sunlight to be able to survive and when covered with sunscreen, no light can get to it.
If you’re not able to get a hold of coral safe sunscreen, the best thing to do is to put sunscreen on one hour before you enter the water. This way most of the sunscreen is soaked into your skin and does not wash off when swimming. Or better yet, prepare for your diving/snorkeling holiday by ordering some coral safe sunscreen beforehand.
As divers and snorkelers, we are able to make a difference. Through our explorations under water, we can raise awareness about the marine environment. We are all fighting to protect our dive and snorkel sites. By telling people what you know after reading this blog post, our impact can continue to be a positive one. Take only memories; leave only bubbles!!!
More information about coral safe sunscreen www.stream2sea.com